Friday, November 30, 2007
Friday, November 30, 2007
Whisky How Long Open Bottle
Friday, November 30, 2007
Wednesday, November 28, 2007
Bloons Tower Defense 4 Ipod Cheats
lectures and exercises of November 28, 2007
hydroxy acids. Succinic acid, malic and tartaric. Lactic acids.




Thursday, November 22, 2007
Vegitable Arrangements
Wednesday, November 21, 2007
lectures and exercises
Functional Groups. Installing and using software in organic chemistry. Main functions. Molecules in 3D. Alcohols to 4 carbon atoms in molecular formula C 4 H 10 O. Structural isomers. Relationship between structure and properties. A fragrance alcohol of formula C H 4 10 O. 10% ethanol solution of 1-butanol, 2-butanol, 2-methyl-1-propanol, 2-methyl-2-propanol.
aldehydes and ketones. Nomenclature.
derivatives of carboxylic acids: esters. Acid component and alcohol component. Nomenclature. Butyl acetate. Butyl butyrate.

Derivatives carboxylic acid: amides. Difference between amines and amides. Resonance. Organic molecules containing the amino group as substituent. Amino acids. Peptides. The amide bond. No rotation around the amide bond.
Alkyl halides.

Introduction to stereoisomerism. Alkenes. 1-butene, 2-butene. Geometrical isomers. The symbols E and Z. Rules of Priority. Applications.
polyenes. Beta-carotene

Thursday, November 15, 2007
Tingling Nipples 1 Week Before Period
Thursday, November 15, 2007
Wednesday, November 14, 2007
What Cheese At East Side Marios
Wednesday 14 November 2007.
Tuesday, November 13, 2007
Where To Buy Soccer Referee Headset
November 27, 2006
1. Write the Lewis structures of the molecules listed below and determine the hybridization of the carbon present. a) carbon dioxide; b) potassium carbonate c) Bromotriclorometano d) Hydrogen cyanide, e) Formaldehyde f) formic acid. (4)
2. Giving names to the molecules described below: (6)

3. The IUPAC name acid threonine protein is present in the acid 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic. Write all possible stereoisomers and indicate those belonging to the series steric L. (5)
4. dicarboxylic acids succinic, malic and tartaric acid are all present in varying amounts in wines. They are 0, 1 and 2 hydroxyl in the structure that contains a total of 4 carbon atoms. Write the structure and give the IUPAC name to all acids. Also indicate the presence of chiral centers and write the corresponding stereoisomers. (8)
5. Indicate the relationship between acid isomers (2S, 3R)-3-fluoro-2-hydroxy butanoic 1 and the structures af. (7)
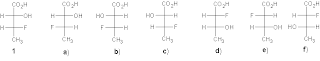
Hinge Pins For Tailgate
written exam of 20 Nov. '06
a . Write the structures of these molecules to
) 2-chloro-3 ,4-diidrossipentanale b) acid 3-amino-2-fluoro-4-nitrobenzoate; c) 2,2,3,3-tetrametilciclobutanone d) ( 2E) -4.5-dimethyl-2-hexene; e) acid (2S, 3R)-2-amino-3-methylpentane; f) How many stereoisomers of the molecule and there)?
2. Identify the functional groups present in vitamin C, whose structure is as follows

3. Write entries for the second acidity increasing the molecules listed below: a) 2-nitrophenol b) phenol, c) 2-methyl-ciclopropanolo d) acid 3-fluorobutanoico e) cloropropanoico acid 2-f) methyl-cyclobutane;
4 . Give an explanation of the fact that cyclohexene reacts rapidly with bromine, while benzene is inert.
5. Write the structure of a) a D-amino acid, b) an L-chetoesoso c) a triglyceride; d) a nucleoside; e) an ester.
Degree Viticulture and Enology January 19, 2006
a . Naming the structures shown.
2. Sort monosaccharides whose structures are given below.
4. How could a separate, 3.5-cyclohexane Tribromo from cyclohexylamine?
5. Write the structures of the following substances: a) a D-amino acid, b) An L-aldopentoso c) The triglyceride formed by acid butyric acid. (6)
degree in Agricultural Science and Technology
Written Examination Organic Chemistry (21 July '05)
1. Write the structures of these molecules
a) 2,3-dihydroxy-4-metilesanale b) (2S) 2-Amino-3-methylpentane; c) dimetilciclobutanolo 1,2-d) (2E, 4Z) -2,4-hexadiene; e) acid, 2,4-dimethyl-3-nitrobenzoate.
2. Draw all possible stereoisomer of 2,3-dihydroxy-butandioco.
3. Write entries for the second increasing acidity of the molecules listed below: a) 2-nitrophenol b) 4-methylphenol; c) 2-methyl-cyclohexanol; d) acid 2-fluoropropanoico e) iodoesanoico acid 3-f) 1, 1.2-trimetilciclopropano.
4. Explain why the hydrocarbon 1,3-cyclopentadiene acts as an acid (pKa ≈ 15) while the cyclopentene no (pKa ≈ 40).
5. Write the structure of a) an L-amino acid, b) a D-chetopentoso c) a monoglyceride d) a nucleotide e) an acetal.
second test exemption ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Degree Viticulture December 18, 2006 and Enology
6. Naming the structures shown, explaining the observed acidity scale.
7. Sort monosaccharides whose structures are given below.
8. Indicate which between chemical species proposed below can be defined as aromatic.
9. Describe a method to separate the 3.5-by 1.3-dietilanilina dietilbenzene.
10. Write the structures of the following substances: a) a dipeptide composed only by D-amino acids b) The anomeric a D-closed form aldotreoso furanosica c) The diglyceride formed by acid butyric acid.
Degree Viticulture and Enology
WRITTEN EXAMINATION ORGANIC CHEMISTRY February 19, 2007
11. Naming molecules below, specifying for each possible number of stereoisomers.
12. Please indicate which features should have an aromatic organic molecule to be defined.
13. Illustrate a method for separating acid from 3-METHYLBENZOQUATE chlorobenzene.
14. Write the generic structures of the following substances: a) a D-aldochetoso b) a b-amino acid, c) the triglyceride formed by acid butyric d) a cyclic hemiacetal, e) a nucleoside present in DNA; f) monounsaturated fatty acid.
15. Write entries for the second growing basicity structures of the molecules shown below. a) Ethylamine b) diisopropylamine; c) Ammonia; d) Aniline e) 4-nitroaniline; f) 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene.
Truco Electric Box Level 41
1. Write the structures of these molecules
a) 3,4-dicloroeptanale b) acid 3-amino-2-chloro-4-etilbenzoico c) 1,2,2-trimetilcicloutanolo d) (2Z)-4-methyl -2 pentene e) 5-metilciclopent en-2-amino-1-f) How many stereoisomers of the molecule and there)?
2. Identify all the functional groups present in vitamin A (retinol), whose structure is as follows.

4. Explain the difference in acidity observed in the propane CH3-CH2-CH3 (pKa = 50) propylene, CH3-CH = CH2 (pKa = 40) and propina CH3-C ≡ CH (pKa = 30).
5. Write the structure of a) an L-amino acid, b) a D-chetoesoso c) a diglyceride d) a nucleoside; e) an ester.
World Of Potato Chips.com Slicers
1. Write the structures of the following molecules:
a) 2,3-dihydroxy-4-metilesanale b) (2S) 2-Amino-3-methylpentane; c) dimetilciclobutanolo 1,2-d) (2E, 4Z) -2,4 hexadiene-e) acid, 2,4-dimethyl-3-nitrobenzoate.
2. Draw all possible stereoisomer of 2,3-dihydroxy butandioco.
3. Write entries for the second increasing acidity of the molecules listed below: a) 2-nitrophenol b) 4-methylphenol; c) 2-methyl-cyclohexanol; d) acid 2-fluoropropanoico e) iodoesanoico acid 3-f) 1, 1.2-trimetilciclopropano.
4. Explain why the hydrocarbon 1,3-cyclopentadiene acts as an acid (pKa ≈ 15) while the cyclopentene no (pKa ≈ 40).
5. Write the structure of a) an L-amino acid, b) a D-chetopentoso c) a monoglyceride d) a nucleotide e) an acetal.
The Family Guy Streaming Subtitles
4 CFU
students must use the address: luilongo@gmail.com
Recommended text:
Objectives: The course
aims to provide the knowledge base of the structural theory of organic molecules in order to understand and interpret the molecular diversity of natural products and those arising from the processing of chemical and enzymatic.
Prerequisites: General Chemistry
Program:
Introduction to organic chemistry. Atoms, the carbon molecules. Orbitals, bonds, hybridization. Lewis formulas. Resonance. Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Classes of organic compounds. Nomenclature. Using Software in organic chemistry. Structural isomers. Cis-trans geometry. Absolute and relative stereochemistry. Chirality. Enantiomers and diastereoisomers. Aromaticity aromatics. Acidity and basicity in organic chemistry. Amino acids, peptides and proteins. Carbohydrates. Acetals. Monosaccharides and polysaccharides. Nucleic Acids. Lipids.










